Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
Globally, India stands second in terms of the generation of Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste with an annual production of 714 million tonnes. However, the total recycling capacity of all the existing plants put together is less than 2%.
This huge imbalance between generation and recycling results in legal/illegal dumping of this valuable waste leading to several social and environmental concerns. On the other hand, India is currently undergoing a severe shortage of pristine aggregates primarily due to an increase in infrastructure development and restrictions on mining activities.
Extraction of high-quality materials such as Recycled Concrete Aggregates (RCA) from C&D waste and utilizing the same in place of natural minerals could resolve the aggregate scarcity issue to a great extent, not to mention other environmental and economic benefits.
In this regard, IITM Civil Engineering researchers, Mr Rohit Prajapati (PhD Scholar), Prof Ravindra Gettu, and Prof Surender Singh as a part of the Centre of Excellence on Technologies for Low-Carbon & Lean Construction have developed a novel approach to beneficiate the RCA waste, employing “Concentrated Solar Energy”, which is a non-conventional and sustainable form of energy. In this method, the waste concrete chunks from C&D waste are heated using concentrated solar energy to reach a temperature of 450-500 °C for 60 minutes followed by cooling of the same under ambient conditions. This process makes the adhered cement mortar very weak, which then could easily be detached from the aggregate’s surface by processing in a ball mill.
The extracted RCA fractions (both coarse aggregates and sand) are found to possess similar physical characteristics to conventionally used civil engineering aggregates.
Incidentally, Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) technology uses mirrors to reflect and concentrate sunlight onto a receiver. The energy from the concentrated sunlight heats the object in the receiver. This heat can be used to generate steam to spin a turbine or power an engine to generate electricity. It can also be used in a variety of industrial applications, like water desalination, enhanced oil recovery, food processing, chemical production, and mineral processing1.
This demonstration involving beneficiation of the RCA was conducted at India One Solar Thermal Power Plant located at Abu Road, Rajasthan (see Fig 1).
References
- Concentrating Solar: Thermal Power Basics,https://www.energy.gov/eere/solar/concentrating-solar-thermal-power-basics
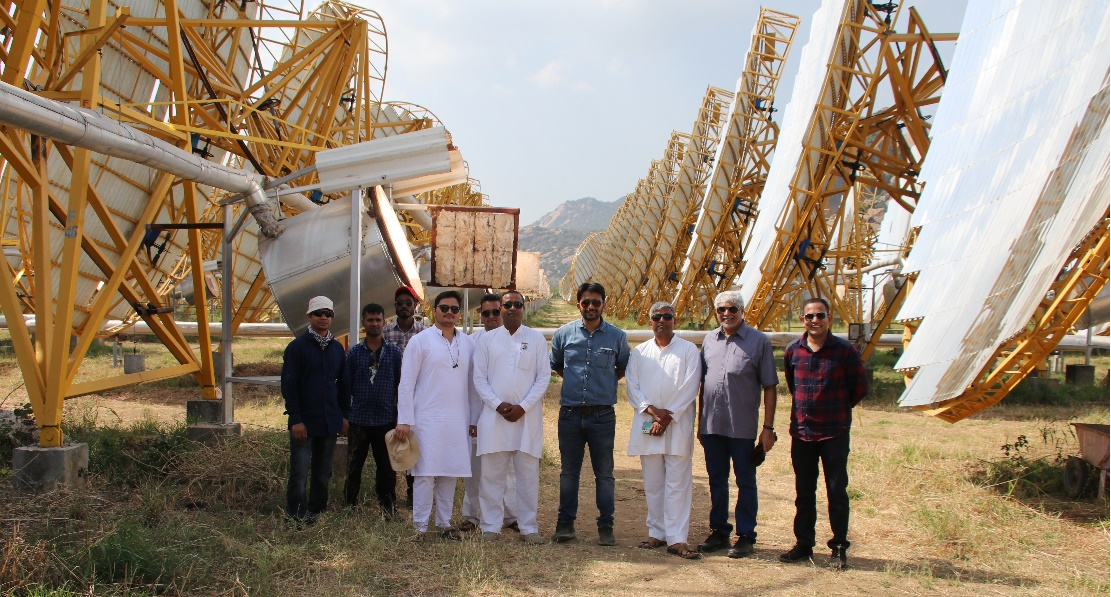

Fig 1 : IITM researchers with India One Solar Thermal Power plant personnel demonstrating the recycling of C&D waste through Concentrated Solar Energy